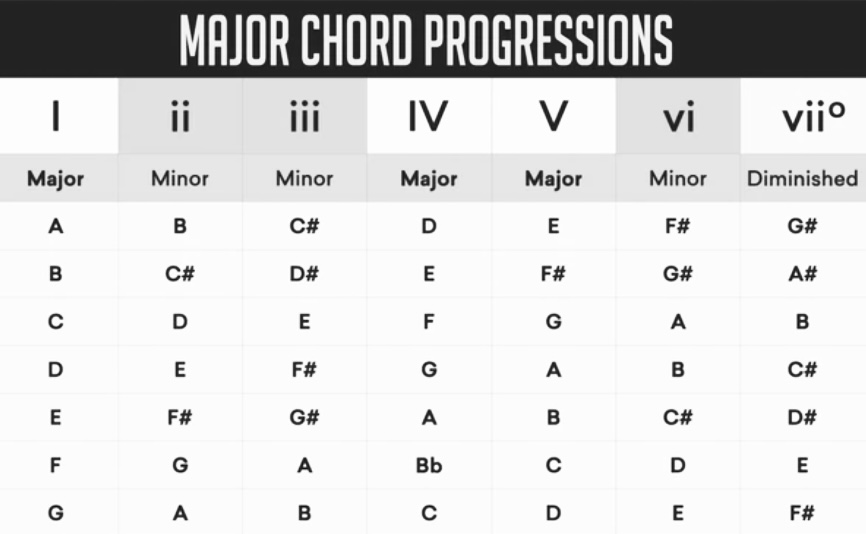
A chord progression is a sequence of chords played in a specific order. It’s like the building blocks of music, giving a song its shape and the vibes that make you feel a certain way. Chord progressions are a fundamental aspect of music theory and are used in various genres, including classical, bollywood, pop, rock, jazz, and more.
Essential elements of a chord progression include:
- Chords: Chords are made up of three or more notes played simultaneously. The most basic chords are triads, consisting of a root note, a third (either major or minor), and a fifth. Chord progressions often involve moving from one chord to another.
- Harmony: Chord progressions create harmony by combining different chords that complement each other. The choice of chords influences the mood and emotion of the music.
- Root Movement: The movement of the root note of each chord determines the direction of the chord progression. The root can move up or down by intervals, creating a sense of tension and resolution.
- Functional Harmony: Chords within a progression often have specific functions, such as tonic (I), subdominant (IV), and dominant (V). These functions contribute to the overall flow and structure of the music.
- Chord progressions can be simple or complex, and they play a crucial role in shaping the emotional and structural aspects of a musical composition. Musicians like to mix them up to create different vibes and feelings in their music.
Examples of common chord progressions include:
- I-IV-V-I: A classic progression providing a strong sense of resolution.
- I-V-vi-IV: Commonly used in pop music, providing a catchy and familiar sound.
- ii-V-I: Widely used in jazz, this progression is known for its smooth and sophisticated sound.